I love some of the new Virtual Reality / Augmented Reality devices coming out (especially CastAR). A couple limitations with the approaches I've seen though is you can't physically touch the environment (video only) and they all require some type of goggles to be worn.
I'm sure there are products in development for special haptic gloves you could wear to simulate touch sensations, but can I build something where the real physical touch is built in? I'd like for the 3-D shape to physically emerge out of the table. In fact there have been a couple movies recently of this in action. If I can find some pictures of those, I'll update this post later with them.
All of my work so far on the servo controller has built up to this goal. Basically I want to make a table top of blocks arranged in a grid pattern that can be individually extruded a controlled distance from the surface. Each block also needs to have its color/image changeable and have some type of touch input. A computer controls the distance of the extrusion, the color/image on the block, and what to do when touch input is detected. (For any patent lovers out there, please consider the ideas in this post public domain prior art.)
To really be useful, I think it needs to have a resolution of 8x8 (Checkers/Chessboard), but I'm starting with a 3x3 prototype - just enough to play Tic Tac Toe.
I'm testing out 3 different block shapes: no taper, low taper, and high taper. If I use an overhead projection to put an image onto the blocks, then the taper will allow me to project images on the sides. I like how the "no taper" will sit flush with the table when fully down though. A collapsible block would probably be best, but that complicates things more than I'd like.
You can see how the low / no taper blocks became unstable near the end of the print and came out rough. I'm going to clean those up later.
Each block has a mount at the bottom that I can tie the servo to.
I then printed the block mount that will sit on top of my servos mount.
That print alone took 15 hours; I was so glad it came out flawless on the first try!
The blocks within the block mount on top of the servo mount...
And a side shot to see the servos beneath...
This is just a progress report. I need to actually move the block mount higher so the servos arms can clear the mount and have plenty of throw. When complete, the servos should be able to go from fully extended to fully flush with the table top.
Not including failed prints, that was 68 hours of 3-D printing!
Showing posts with label arduino. Show all posts
Showing posts with label arduino. Show all posts
Sunday, January 10, 2016
Saturday, October 3, 2015
Servo Controller: Binary Serial Communication (Computer Side)
My previous post discussed the receiving end of the serial communications; now I'll cover the sending side.
My starting point was my Servo Control via .NET application described a couple posts ago. It already had the framework for sending and receiving over the serial port, so we just need to make the adjustments for binary.
First to change is the UI. The text input field and send button has been replaced by 3 buttons, 9 track bars, and 18 numeric up/down controls.
The buttons are named as follows:
btnAllDown, btnAllMiddle, btnAllUp
The track bars are named as follows (range 0 to 100):
trackBar11, trackBar12, trackBar13, trackBar21, trackBar22, trackBar23, trackBar31, trackBar32, trackBar33
The numeric up/downs are named as follows (range 0 to 4096):
nudServoLowerLimit11, nudServoLowerLimit12, nudServoLowerLimit13, nudServoLowerLimit21, nudServoLowerLimit22, nudServoLowerLimit23, nudServoLowerLimit31, nudServoLowerLimit32, nudServoLowerLimit33
nudServoUpperLimit11, nudServoUpperLimit12, nudServoUpperLimit13, nudServoUpperLimit21, nudServoUpperLimit22, nudServoUpperLimit23, nudServoUpperLimit31, nudServoUpperLimit32, nudServoUpperLimit33
Next I defined the structure that will be sent over the serial line. This structure must match the one on the receiving end. Since this structure will be reused for several commands, I have the first byte be the command and a built-in getBytes() function for convenience.
Warning! The Marshal commands in .NET will create a byte array for a given structure. However, by default the byte array created will reserve 2 bytes for any variables listed as a Byte (the structure below would be 6 bytes in length). For it to be compatible with the Arduino side of the communication, we must tag the structure "LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack :=1". Now a Byte variable will be treated as 1 byte and the structure returned will be 5 bytes in length.
' Must set Sequential with Pack = 1 so .NET creates a byte array
' with the Byte as 1 byte (and not as 2).
<StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack:=1)> _
Public Structure CommandSetServoValueStructure
Public command As Byte
Public servoNumber As UInt16
Public newValue As UInt16
Public Function getBytes() As Byte()
Dim binaryBytes(5) As Byte
Dim pointerCommand As IntPtr = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(Marshal.SizeOf(Me))
Marshal.StructureToPtr(Me, pointerCommand, False)
Marshal.Copy(pointerCommand, binaryBytes, 0, Marshal.SizeOf(Me))
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pointerCommand)
Return binaryBytes
End Function
End Structure
Each command will fill out the values of this structure. Sending it over the network is then a simple:
Dim thisCommand As CommandSetServoValueStructure
' Fill in thisCommand as appropriate.
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = thisCommand.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Private Sub sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(ByVal servoNumber As Integer, ByVal value_percent As Integer)
Try
Dim commandSetServoPercent As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoPercent.command = 1
commandSetServoPercent.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoPercent.newValue = value_percent
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoPercent.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
The top numeric up/down sets the upper range for the servo.
Private Sub sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(ByVal servoNumber As Integer, ByVal newUpper_pulseLength As Integer)
Try
Dim commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.command = 2
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.newValue = newUpper_pulseLength
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(0, nudServoUpperLimit11.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(1, nudServoUpperLimit21.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(2, nudServoUpperLimit31.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(3, nudServoUpperLimit12.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(4, nudServoUpperLimit22.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(5, nudServoUpperLimit32.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(6, nudServoUpperLimit13.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(7, nudServoUpperLimit23.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(8, nudServoUpperLimit33.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
The bottom numeric up/down sets the lower range for the servo.
Private Sub sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(ByVal servoNumber As Integer, ByVal newLower_pulseLength As Integer)
Try
Dim commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.command = 3
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.newValue = newLower_pulseLength
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(0, nudServoLowerLimit11.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(1, nudServoLowerLimit21.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(2, nudServoLowerLimit31.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(3, nudServoLowerLimit12.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(4, nudServoLowerLimit22.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(5, nudServoLowerLimit32.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(6, nudServoLowerLimit13.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(7, nudServoLowerLimit23.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(8, nudServoLowerLimit33.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
The set all buttons are just shortcuts for changing every track bar to 0%, 50%, or 100%.
Private Sub setAll(ByVal newValue_percent As Integer)
Try
trackBar11.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar21.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar31.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar12.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar22.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar32.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar13.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar23.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar33.Value = newValue_percent
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllDown_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllDown.Click
Try
setAll(0)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllMiddle_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllMiddle.Click
Try
setAll(50)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllUp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllUp.Click
Try
setAll(100)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Imports System
Imports System.IO.Ports
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Public Class FormMain
Private _isInitializingForm As Boolean = True
Private _isLoadingConfiguration As Boolean = False
Public ReadOnly Property isPopulatingSettings As Boolean
Get
If _isInitializingForm Then
Return True
End If
If _isLoadingConfiguration Then
Return True
End If
Return False
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Definite a delegate to transfer incoming data from the background
''' (serial) thread to the foreground (UI) thread.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Delegate Sub ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
''' <summary>
''' The serial port object that will communicate.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private WithEvents connectedSerialPort As New SerialPort()
Public Sub New()
' This call is required by the designer.
InitializeComponent()
' Add any initialization after the InitializeComponent() call.
_isInitializingForm = False
End Sub
Private Sub loadConfigurationValues()
Try
_isLoadingConfiguration = True
Try
nudServoUpperLimit11.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit12.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit13.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit21.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit22.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit23.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit31.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit32.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit33.Value = 550
nudServoLowerLimit11.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit12.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit13.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit21.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit22.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit23.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit31.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit32.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit33.Value = 200
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
_isLoadingConfiguration = False
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub FormMain_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Try
loadConfigurationValues()
refreshPortsList()
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
' Port is found, attempt to connect to it.
connectSerialPort()
Else
' Update which controls are enabled (so disconnect button is disabled at startup).
updateConnectedEnableFields()
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnConnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnConnect.Click
Try
connectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnDisconnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnDisconnect.Click
Try
disconnectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_DataReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.DataReceived
Try
' Received data from the serial port, send it for processing.
processIncomingData(connectedSerialPort.ReadExisting())
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_ErrorReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialErrorReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.ErrorReceived
Try
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnRefreshPorts_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnRefreshPorts.Click
Try
refreshPortsList()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Returns if the serial port is currently connected.
''' </summary>
''' <value></value>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private ReadOnly Property isSerialPortConnected
Get
Return connectedSerialPort.IsOpen()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Update whether or not each UI control should be enabled based on
''' the connection state.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub updateConnectedEnableFields()
Try
Dim isConnected As Boolean = isSerialPortConnected
btnConnect.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnDisconnect.Enabled = isConnected
ddlCOMPort.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnRefreshPorts.Enabled = Not isConnected
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Connect to the selected serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub connectSerialPort()
Try
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
connectedSerialPort.PortName = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
connectedSerialPort.BaudRate = 9600
connectedSerialPort.WriteTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadBufferSize = 4096
connectedSerialPort.WriteBufferSize = 2048
connectedSerialPort.Parity = IO.Ports.Parity.None
connectedSerialPort.StopBits = IO.Ports.StopBits.One
connectedSerialPort.DataBits = 8
connectedSerialPort.Open()
'Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000)
' Send Extended ASCII Code 128 for binary mode.
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = {128}
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 1)
End If
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Disconnect the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub disconnectSerialPort()
Try
connectedSerialPort.Close()
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Detect available serial ports and update the COM port list.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub refreshPortsList()
Try
' Keep track of the selected port so we can reselect it after fresh.
Dim currentlySelectedPort As String = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
' Get the available ports and update the dropdown list.
Dim availablePorts As Array = IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames()
ddlCOMPort.Items.Clear()
ddlCOMPort.Items.AddRange(availablePorts)
' Reselect the previously selected port as a default.
If currentlySelectedPort IsNot Nothing Then
If ddlCOMPort.Items.Contains(currentlySelectedPort) Then
ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem = currentlySelectedPort
End If
End If
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = -1 AndAlso ddlCOMPort.Items.Count > 0 Then
' No port selected but one is available, default to it.
ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = 0
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Function to process incoming data from the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub processIncomingData(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
Try
If txtReceive.InvokeRequired Then
' On background (serial port) thread. Invoke a delegate to call this
' function again on the foreground (UI) thread.
Dim incomingTextDelegate As New ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(AddressOf processIncomingData)
Me.Invoke(incomingTextDelegate, New Object() {incomingBuffer})
Else
' On foreground (UI) thread. Process the message.
txtReceive.Text += incomingBuffer
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
' ---------- CODE FROM ABOVE ----------
End Class
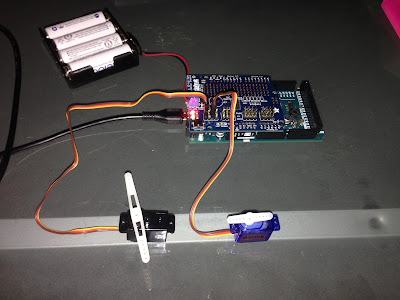
At startup...
The Board Manager automatically connects to the first COM port it detects and sends the binary input command.
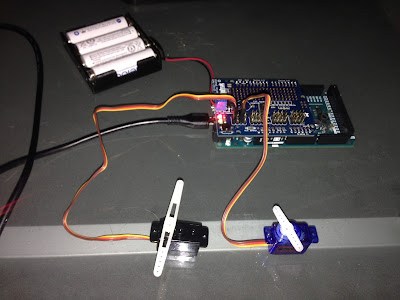
Setting some of the servo values...
And the servos in action...
Copyright (c) 2015 Clinton Kam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
My starting point was my Servo Control via .NET application described a couple posts ago. It already had the framework for sending and receiving over the serial port, so we just need to make the adjustments for binary.
First to change is the UI. The text input field and send button has been replaced by 3 buttons, 9 track bars, and 18 numeric up/down controls.
The buttons are named as follows:
btnAllDown, btnAllMiddle, btnAllUp
The track bars are named as follows (range 0 to 100):
trackBar11, trackBar12, trackBar13, trackBar21, trackBar22, trackBar23, trackBar31, trackBar32, trackBar33
The numeric up/downs are named as follows (range 0 to 4096):
nudServoLowerLimit11, nudServoLowerLimit12, nudServoLowerLimit13, nudServoLowerLimit21, nudServoLowerLimit22, nudServoLowerLimit23, nudServoLowerLimit31, nudServoLowerLimit32, nudServoLowerLimit33
nudServoUpperLimit11, nudServoUpperLimit12, nudServoUpperLimit13, nudServoUpperLimit21, nudServoUpperLimit22, nudServoUpperLimit23, nudServoUpperLimit31, nudServoUpperLimit32, nudServoUpperLimit33
Next I defined the structure that will be sent over the serial line. This structure must match the one on the receiving end. Since this structure will be reused for several commands, I have the first byte be the command and a built-in getBytes() function for convenience.
Warning! The Marshal commands in .NET will create a byte array for a given structure. However, by default the byte array created will reserve 2 bytes for any variables listed as a Byte (the structure below would be 6 bytes in length). For it to be compatible with the Arduino side of the communication, we must tag the structure "LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack :=1". Now a Byte variable will be treated as 1 byte and the structure returned will be 5 bytes in length.
' Must set Sequential with Pack = 1 so .NET creates a byte array
' with the Byte as 1 byte (and not as 2).
<StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential, Pack:=1)> _
Public Structure CommandSetServoValueStructure
Public command As Byte
Public servoNumber As UInt16
Public newValue As UInt16
Public Function getBytes() As Byte()
Dim binaryBytes(5) As Byte
Dim pointerCommand As IntPtr = Marshal.AllocHGlobal(Marshal.SizeOf(Me))
Marshal.StructureToPtr(Me, pointerCommand, False)
Marshal.Copy(pointerCommand, binaryBytes, 0, Marshal.SizeOf(Me))
Marshal.FreeHGlobal(pointerCommand)
Return binaryBytes
End Function
End Structure
Each command will fill out the values of this structure. Sending it over the network is then a simple:
Dim thisCommand As CommandSetServoValueStructure
' Fill in thisCommand as appropriate.
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = thisCommand.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Write takes in the bytes to send, the starting index, and the number of bytes to send - which in our cause is the size of our structure.
Each track bar sets the servo's position by percentage (from 0 to 100).
Try
Dim commandSetServoPercent As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoPercent.command = 1
commandSetServoPercent.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoPercent.newValue = value_percent
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoPercent.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub trackBar33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles trackBar33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Setting Servo Range
Command 2: Setting the Servo Upper Limit
The top numeric up/down sets the upper range for the servo.
Private Sub sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(ByVal servoNumber As Integer, ByVal newUpper_pulseLength As Integer)
Try
Dim commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.command = 2
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.newValue = newUpper_pulseLength
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoUpperLimit_pulseLength.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(0, nudServoUpperLimit11.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(1, nudServoUpperLimit21.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(2, nudServoUpperLimit31.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(3, nudServoUpperLimit12.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(4, nudServoUpperLimit22.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(5, nudServoUpperLimit32.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(6, nudServoUpperLimit13.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(7, nudServoUpperLimit23.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoUpperLimit33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoUpperLimit33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoUpperLimitToSerial(8, nudServoUpperLimit33.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Command 3: Setting the Servo Lower Limit
The bottom numeric up/down sets the lower range for the servo.
Private Sub sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(ByVal servoNumber As Integer, ByVal newLower_pulseLength As Integer)
Try
Dim commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength As CommandSetServoValueStructure
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.command = 3
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.servoNumber = servoNumber
commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.newValue = newLower_pulseLength
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = commandSetServoLowerLimit_pulseLength.getBytes
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 5)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit11_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit11.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(0, nudServoLowerLimit11.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(0, trackBar11.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit21_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit21.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(1, nudServoLowerLimit21.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(1, trackBar21.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit31_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit31.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(2, nudServoLowerLimit31.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(2, trackBar31.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit12_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit12.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(3, nudServoLowerLimit12.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(3, trackBar12.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit22_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit22.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(4, nudServoLowerLimit22.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(4, trackBar22.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit32_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit32.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(5, nudServoLowerLimit32.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(5, trackBar32.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit13_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit13.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(6, nudServoLowerLimit13.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(6, trackBar13.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit23_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit23.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(7, nudServoLowerLimit23.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(7, trackBar23.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub nudServoLowerLimit33_ValueChanged(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles nudServoLowerLimit33.ValueChanged
Try
If Not isPopulatingSettings Then
sendCommandSetServoLowerLimitToSerial(8, nudServoLowerLimit33.Value)
sendCommandSetServoPercentToSerial(8, trackBar33.Value)
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Set All
The set all buttons are just shortcuts for changing every track bar to 0%, 50%, or 100%.
Private Sub setAll(ByVal newValue_percent As Integer)
Try
trackBar11.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar21.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar31.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar12.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar22.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar32.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar13.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar23.Value = newValue_percent
trackBar33.Value = newValue_percent
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllDown_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllDown.Click
Try
setAll(0)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllMiddle_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllMiddle.Click
Try
setAll(50)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnAllUp_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnAllUp.Click
Try
setAll(100)
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Additional Support Code
Imports System
Imports System.IO.Ports
Imports System.Runtime.InteropServices
Public Class FormMain
Private _isInitializingForm As Boolean = True
Private _isLoadingConfiguration As Boolean = False
Public ReadOnly Property isPopulatingSettings As Boolean
Get
If _isInitializingForm Then
Return True
End If
If _isLoadingConfiguration Then
Return True
End If
Return False
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Definite a delegate to transfer incoming data from the background
''' (serial) thread to the foreground (UI) thread.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Delegate Sub ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
''' <summary>
''' The serial port object that will communicate.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private WithEvents connectedSerialPort As New SerialPort()
Public Sub New()
' This call is required by the designer.
InitializeComponent()
' Add any initialization after the InitializeComponent() call.
_isInitializingForm = False
End Sub
Private Sub loadConfigurationValues()
Try
_isLoadingConfiguration = True
Try
nudServoUpperLimit11.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit12.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit13.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit21.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit22.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit23.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit31.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit32.Value = 550
nudServoUpperLimit33.Value = 550
nudServoLowerLimit11.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit12.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit13.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit21.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit22.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit23.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit31.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit32.Value = 200
nudServoLowerLimit33.Value = 200
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
_isLoadingConfiguration = False
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub FormMain_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Try
loadConfigurationValues()
refreshPortsList()
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
' Port is found, attempt to connect to it.
connectSerialPort()
Else
' Update which controls are enabled (so disconnect button is disabled at startup).
updateConnectedEnableFields()
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnConnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnConnect.Click
Try
connectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnDisconnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnDisconnect.Click
Try
disconnectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_DataReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.DataReceived
Try
' Received data from the serial port, send it for processing.
processIncomingData(connectedSerialPort.ReadExisting())
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_ErrorReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialErrorReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.ErrorReceived
Try
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnRefreshPorts_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnRefreshPorts.Click
Try
refreshPortsList()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Returns if the serial port is currently connected.
''' </summary>
''' <value></value>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private ReadOnly Property isSerialPortConnected
Get
Return connectedSerialPort.IsOpen()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Update whether or not each UI control should be enabled based on
''' the connection state.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub updateConnectedEnableFields()
Try
Dim isConnected As Boolean = isSerialPortConnected
btnConnect.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnDisconnect.Enabled = isConnected
ddlCOMPort.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnRefreshPorts.Enabled = Not isConnected
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Connect to the selected serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub connectSerialPort()
Try
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
connectedSerialPort.PortName = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
connectedSerialPort.BaudRate = 9600
connectedSerialPort.WriteTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadBufferSize = 4096
connectedSerialPort.WriteBufferSize = 2048
connectedSerialPort.Parity = IO.Ports.Parity.None
connectedSerialPort.StopBits = IO.Ports.StopBits.One
connectedSerialPort.DataBits = 8
connectedSerialPort.Open()
'Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000)
' Send Extended ASCII Code 128 for binary mode.
Dim binaryBytes() As Byte = {128}
connectedSerialPort.Write(binaryBytes, 0, 1)
End If
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Disconnect the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub disconnectSerialPort()
Try
connectedSerialPort.Close()
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Detect available serial ports and update the COM port list.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub refreshPortsList()
Try
' Keep track of the selected port so we can reselect it after fresh.
Dim currentlySelectedPort As String = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
' Get the available ports and update the dropdown list.
Dim availablePorts As Array = IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames()
ddlCOMPort.Items.Clear()
ddlCOMPort.Items.AddRange(availablePorts)
' Reselect the previously selected port as a default.
If currentlySelectedPort IsNot Nothing Then
If ddlCOMPort.Items.Contains(currentlySelectedPort) Then
ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem = currentlySelectedPort
End If
End If
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = -1 AndAlso ddlCOMPort.Items.Count > 0 Then
' No port selected but one is available, default to it.
ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = 0
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Function to process incoming data from the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub processIncomingData(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
Try
If txtReceive.InvokeRequired Then
' On background (serial port) thread. Invoke a delegate to call this
' function again on the foreground (UI) thread.
Dim incomingTextDelegate As New ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(AddressOf processIncomingData)
Me.Invoke(incomingTextDelegate, New Object() {incomingBuffer})
Else
' On foreground (UI) thread. Process the message.
txtReceive.Text += incomingBuffer
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
' ---------- CODE FROM ABOVE ----------
End Class
In Operation
At startup...
The Board Manager automatically connects to the first COM port it detects and sends the binary input command.
Setting some of the servo values...
And the servos in action...
Copyright (c) 2015 Clinton Kam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Wednesday, September 23, 2015
Servo Controller: Binary Serial Communication (Arduino Side)
ASCII vs Binary
ASCII text communication is convenient for debugging, but it's not particular efficient. The microcontroller is having to take a string of characters, convert those strings into numbers, then process the instructions of those numbers.
For example, set servo 12 to a value of 50 percent:
s=12
p=50
Total 10 bytes as ASCII (including carriage returns).
Binary communication is much more efficient. A pointer can be used to interpret the array of bytes as a structure, so there is no CPU expensive conversions from strings to numbers. And where ASCII would take 5 bytes to represent 65535, binary would need just 2.
Let's define a structure for commands...
const int16_t commandLength_bytes = 5;
struct CommandSetServoValueStructure
{
byte command;
uint16_t servoNumber;
uint16_t newValue;
// Must denote structure as packed for variables to be
// properly interpreted from a byte array.
} __attribute__((__packed__));
We'll say command 1 is to set a percent value.
So now the byte array looks like:
Total 5 bytes as binary.5 bytes instead of 10!
But let's make the example more interesting. We'll say command 2 is to set an upper pulse value. We want to control servo 10,000 to a pulse value of 1100.
That byte array looks like:
[2][16][39][76][4]
Total 5 bytes as binary.
As a string it would have been:
s=10000
u=1100
Total 15 bytes as ASCII (includes carriage returns).
5 bytes instead of 15!
Now imagine we were sending 10,000 servo commands, saving 10 bytes per command. 100 KB is a nice savings over a serial cable.
That saves on the amount of data we're sending over, but what about interpreting the data? String manipulation is a (relatively) slow process. In C, you can use a pointer to interpret that array of bytes as whatever structure you wish.
Say the incoming data is stored in an array...
byte *incomingCommand;
Use a pointer to interpret that array of bytes as our desired structure...
CommandSetServoValueStructure *commandSetServoPercent = (CommandSetServoValueStructure *)incomingCommand;
Then you can dereference the values from the structure to read them...
commandSetServoPercent->servoNumber
commandSetServoPercent->newValue
In the examples above I listed out the byte array for values such as 12 - [12][0] and 10,000 - [16][39]. But why is it [12][0] and not [0][12] and where do you get 16 and 39 from 10,000?
[Byte 1][Byte 2][Byte 3][Byte 4]
or
[Byte 4][Byte 3][Byte 2][Byte 1]
The order is known as Endianness. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endianness
The computer your code is running on could order variables either way. It doesn't matter which order is used, just so long as both ends of the communication use the same one. Swapping the order of the bytes is trivial, and there are plenty of examples around on how to do that. Since my .NET application and my Arduino use the same byte order, I didn't have to do any byte swapping.
I've switched to Programmer mode, selected "Dec", and typed in 10000.
I then opened 2 more Calculators; entering the "more significant" byte into one and the "less significant" byte into the other. Now you can see where the 16 and 39 mentioned earlier come from!
Rather than lose the ASCII debugging mode, I'm going to modify the code to support both kinds of input. When the microcontroller first starts, if the user presses the ENTER key (new line), then it goes into ASCII mode. If the program sends a character code of 128 (an extended code a user is unlikely to type), then it goes into binary mode.
Reading Binary
In the examples above I listed out the byte array for values such as 12 - [12][0] and 10,000 - [16][39]. But why is it [12][0] and not [0][12] and where do you get 16 and 39 from 10,000?
Byte Order
With a variable consisting of more than 1 byte, there are two ways it can be ordered:[Byte 1][Byte 2][Byte 3][Byte 4]
or
[Byte 4][Byte 3][Byte 2][Byte 1]
The order is known as Endianness. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endianness
The computer your code is running on could order variables either way. It doesn't matter which order is used, just so long as both ends of the communication use the same one. Swapping the order of the bytes is trivial, and there are plenty of examples around on how to do that. Since my .NET application and my Arduino use the same byte order, I didn't have to do any byte swapping.
Parsing a Number with >1 Bytes
Windows Calculator has a Programmer mode (under the View menu) that comes in very handy.I've switched to Programmer mode, selected "Dec", and typed in 10000.
I then opened 2 more Calculators; entering the "more significant" byte into one and the "less significant" byte into the other. Now you can see where the 16 and 39 mentioned earlier come from!
Dual Input Modes
Rather than lose the ASCII debugging mode, I'm going to modify the code to support both kinds of input. When the microcontroller first starts, if the user presses the ENTER key (new line), then it goes into ASCII mode. If the program sends a character code of 128 (an extended code a user is unlikely to type), then it goes into binary mode.
Define an enumeration for the input modes and create a variable to keep track of what we're in...
enum inputModes
{
InputModeUndefined = 0,
InputModeASCII = 1,
InputModeBinary = 2
};
int16_t inputMode = InputModeUndefined;
The main program loop of the Arduino continuously checks if data is available over the Serial line. If the input mode has never been defined, then it calls getSerialInputMode() to determine which input it is in. After the input mode has been determined, it will route all incoming Serial input to the appropriate parser - getSerialASCIICommand() or getSerialBinaryCommand().
void loop()
{
// First input will be the mode to be in: binary or text
// Once the flag is set we'll send the serial input to the
// appropriate processor.
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
switch (inputMode)
{
case InputModeUndefined:
getSerialInputMode();
break;
case InputModeASCII:
getSerialASCIICommand();
break;
case InputModeBinary:
getSerialBinaryCommand();
break;
}
}
return;
}
void getSerialInputMode()
{
int16_t incomingByte = Serial.read();
switch (incomingByte)
{
case 10: // New Line
Serial.println("ASCII Input Mode");
inputMode = InputModeASCII;
break;
case 128: // Extended ASCII Code
Serial.println("Binary Input Mode");
inputMode = InputModeBinary;
break;
default:
Serial.println("Send 'New Line' for ASCII Input Mode.");
break;
}
return;
}
The getSerialASCIICommand() function is basically how the commands were parsed before.
void getSerialASCIICommand()
{
String serialInputString = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
// Echo back the command.
Serial.println(serialInputString);
if (serialInputString.startsWith("s=")) // Servo
{
String servoNumberString = serialInputString.substring(2);
debugServoNumber = servoNumberString.toInt();
Serial.print("Debug servo:");
Serial.println(debugServoNumber);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("p=")) // Percent Value
{
String valuePercentString = serialInputString.substring(2);
float newValue_percent = valuePercentString.toFloat();
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_percent(newValue_percent);
Serial.print("Set percent:");
Serial.println(newValue_percent);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("v=")) // Pulse Value
{
String pulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
uint16_t newPulseValue = pulseValueString.toInt();
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_pulseLength(newPulseValue);
Serial.print("Set pulse:");
Serial.println(newPulseValue);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("u=")) // Upper Pulse Value
{
String upperPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
uint16_t newUpperPulseValue = upperPulseValueString.toInt();
servos[debugServoNumber].setUpperPulseLength(newUpperPulseValue);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMaximumValue();
Serial.print("Set upper pulse:");
Serial.println(newUpperPulseValue);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("l=")) // Lower Pulse Value
{
String lowerPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
uint16_t newLowerPulseValue = lowerPulseValueString.toInt();
servos[debugServoNumber].setLowerPulseLength(newLowerPulseValue);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMinimumValue();
Serial.print("Set lower pulse:");
Serial.println(newLowerPulseValue);
}
return;
}
The getSerialBinaryCommand() is the new code. We'll define a byte array and a variable to keep track of where we are in that array.
byte incomingBytes[commandLength_bytes];
int16_t incomingBytePosition = 0;
Upon receiving a byte over the Serial line, it stores it in the byte array and increments the position. The very first byte of the array is the command. So once we get that first byte, we can determine if we've received enough bytes for our structure and then process as appropriate. For now all the commands use the same structure and thus are the same length. However, that will very likely change in the future with more advanced commands.
void getSerialBinaryCommand()
{
incomingBytes[incomingBytePosition] = Serial.read();
incomingBytePosition += 1;
switch(incomingBytes[0])
{
case 0:
// Reset Commands
// If the controller gets in an unsynchronized state with the
// serial commands, then it can send a series of all 0s to
// reset to a new command. The number of 0s required would vary
// by the size of the command structure the controller thinks
// we're populating (and how far into that structure it thinks
// we have populated). Once we get out of populating the structure,
// the subsequent "0" bytes just continue to fall into this code
// and are handled fine.
// Reset incoming array position for next command.
incomingBytePosition = 0;
break;
case 1:
if (incomingBytePosition >= commandLength_bytes)
{
processCommandSetServoPercent(&incomingBytes[0]);
// Reset incoming array position for next command.
incomingBytePosition = 0;
}
break;
case 2:
if (incomingBytePosition >= commandLength_bytes)
{
processCommandSetServoUpperLimit(&incomingBytes[0]);
// Reset incoming array position for next command.
incomingBytePosition = 0;
}
break;
case 3:
if (incomingBytePosition >= commandLength_bytes)
{
processCommandSetServoLowerLimit(&incomingBytes[0]);
// Reset incoming array position for next command.
incomingBytePosition = 0;
}
break;
}
return;
}
Processing each command is very efficient: Interpret the incoming bytes as a structure, then read the values.
void processCommandSetServoPercent(byte *incomingCommand)
{
CommandSetServoValueStructure *commandSetServoPercent = (CommandSetServoValueStructure *)incomingCommand;
if (commandSetServoPercent->servoNumber >= 0 &&
commandSetServoPercent->servoNumber < numberOfServos)
{
servos[commandSetServoPercent->servoNumber].setToValue_percent((float)commandSetServoPercent->newValue);
}
return;
}
void processCommandSetServoUpperLimit(byte *incomingCommand)
{
CommandSetServoValueStructure *commandSetServoUpperLimit = (CommandSetServoValueStructure *)incomingCommand;
if (commandSetServoUpperLimit->servoNumber >= 0 &&
commandSetServoUpperLimit->servoNumber < numberOfServos)
{
servos[commandSetServoUpperLimit->servoNumber].setUpperPulseLength((float)commandSetServoUpperLimit->newValue);
}
return;
}
void processCommandSetServoLowerLimit(byte *incomingCommand)
{
CommandSetServoValueStructure *commandSetServoLowerLimit = (CommandSetServoValueStructure *)incomingCommand;
if (commandSetServoLowerLimit->servoNumber >= 0 &&
commandSetServoLowerLimit->servoNumber < numberOfServos)
{
servos[commandSetServoLowerLimit->servoNumber].setLowerPulseLength((float)commandSetServoLowerLimit->newValue);
}
return;
}
Copyright (c) 2015 Clinton Kam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Sunday, August 16, 2015
Servo Controller: Servo Control via .NET Application
Using the Serial Monitor in the Arduino IDE was convenient for quick testing, but ultimately I want a custom application to control all my servos. So my next step was to recreate the Serial Monitor as my own application (that I could eventually expand upon).
I created a very simple VB.NET application to communicate over a serial port. A couple notes on it:
- The program automatically connects to the first COM port it finds. That's generally pretty safe as nowadays the average computer user doesn't have any devices that communicate over a serial port. (Ahh, I remember back in the day, before USB, when you plugged the mouse into a COM port. Or Doom over serial, good times.) This automatic connection is dangerous if you do have devices such as 3-D printers that communicate over a COM port.
- The baud rate and similar are hard coded to match my Arduino code, but you may want to expose that as a configurable item.
The first dropdown list is for the COM port (automatically selected to the first found at startup). It is named ddlCOMPort.
The buttons from left to right are: btnConnect, btnDisconnect, btnRefreshPorts, btnClear, and btnSend.
The input text box is txtSend, and the output read-only text box is txtReceive.
Imports System.IO.Ports
Public Class FormMain
''' <summary>
''' Definite a delegate to transfer incoming data from the background
''' (serial) thread to the foreground (UI) thread.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Delegate Sub ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
''' <summary>
''' The serial port object that will communicate.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private WithEvents connectedSerialPort As New SerialPort()
Public Sub New()
' This call is required by the designer.
InitializeComponent()
' Add any initialization after the InitializeComponent() call.
End Sub
Private Sub FormMain_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Try
refreshPortsList()
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
' Port is found, attempt to connect to it.
connectSerialPort()
Else
' Update which controls are enabled (so disconnect button is disabled at startup).
updateConnectedEnableFields()
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnConnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnConnect.Click
Try
connectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnDisconnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnDisconnect.Click
Try
disconnectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnSend_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnSend.Click
Try
connectedSerialPort.Write(txtSend.Text + vbCrLf)
txtSend.Text = ""
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_DataReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.DataReceived
Try
' Received data from the serial port, send it for processing.
processIncomingData(connectedSerialPort.ReadExisting())
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_ErrorReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialErrorReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.ErrorReceived
Try
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnRefreshPorts_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnRefreshPorts.Click
Try
refreshPortsList()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnClear_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnClear.Click
Try
txtReceive.Text = ""
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Returns if the serial port is currently connected.
''' </summary>
''' <value></value>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private ReadOnly Property isSerialPortConnected
Get
Return connectedSerialPort.IsOpen()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Update whether or not each UI control should be enabled based on
''' the connection state.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub updateConnectedEnableFields()
Try
Dim isConnected As Boolean = isSerialPortConnected
btnConnect.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnDisconnect.Enabled = isConnected
ddlCOMPort.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnRefreshPorts.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnSend.Enabled = isConnected
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Connect to the selected serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub connectSerialPort()
Try
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
connectedSerialPort.PortName = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
connectedSerialPort.BaudRate = 9600
connectedSerialPort.WriteTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadBufferSize = 4096
connectedSerialPort.WriteBufferSize = 2048
connectedSerialPort.Parity = IO.Ports.Parity.None
connectedSerialPort.StopBits = IO.Ports.StopBits.One
connectedSerialPort.DataBits = 8
connectedSerialPort.Open()
End If
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Disconnect the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub disconnectSerialPort()
Try
connectedSerialPort.Close()
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Detect available serial ports and update the COM port list.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub refreshPortsList()
Try
' Keep track of the selected port so we can reselect it after fresh.
Dim currentlySelectedPort As String = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
' Get the available ports and update the dropdown list.
Dim availablePorts As Array = IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames()
ddlCOMPort.Items.Clear()
ddlCOMPort.Items.AddRange(availablePorts)
' Reselect the previously selected port as a default.
If currentlySelectedPort IsNot Nothing Then
If ddlCOMPort.Items.Contains(currentlySelectedPort) Then
ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem = currentlySelectedPort
End If
End If
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = -1 AndAlso ddlCOMPort.Items.Count > 0 Then
' No port selected but one is available, default to it.
ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = 0
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Function to process incoming data from the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub processIncomingData(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
Try
If txtReceive.InvokeRequired Then
' On background (serial port) thread. Invoke a delegate to call this
' function again on the foreground (UI) thread.
Dim incomingTextDelegate As New ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(AddressOf processIncomingData)
Me.Invoke(incomingTextDelegate, New Object() {incomingBuffer})
Else
' On foreground (UI) thread. Process the message.
txtReceive.Text += incomingBuffer
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
End Class
I created a very simple VB.NET application to communicate over a serial port. A couple notes on it:
- The program automatically connects to the first COM port it finds. That's generally pretty safe as nowadays the average computer user doesn't have any devices that communicate over a serial port. (Ahh, I remember back in the day, before USB, when you plugged the mouse into a COM port. Or Doom over serial, good times.) This automatic connection is dangerous if you do have devices such as 3-D printers that communicate over a COM port.
- The baud rate and similar are hard coded to match my Arduino code, but you may want to expose that as a configurable item.
The application in action:
The application in Visual Studio's designer:
The first dropdown list is for the COM port (automatically selected to the first found at startup). It is named ddlCOMPort.
The buttons from left to right are: btnConnect, btnDisconnect, btnRefreshPorts, btnClear, and btnSend.
The input text box is txtSend, and the output read-only text box is txtReceive.
The code:
Imports System.IO.Ports
Public Class FormMain
''' <summary>
''' Definite a delegate to transfer incoming data from the background
''' (serial) thread to the foreground (UI) thread.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Delegate Sub ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
''' <summary>
''' The serial port object that will communicate.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private WithEvents connectedSerialPort As New SerialPort()
Public Sub New()
' This call is required by the designer.
InitializeComponent()
' Add any initialization after the InitializeComponent() call.
End Sub
Private Sub FormMain_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Try
refreshPortsList()
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
' Port is found, attempt to connect to it.
connectSerialPort()
Else
' Update which controls are enabled (so disconnect button is disabled at startup).
updateConnectedEnableFields()
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnConnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnConnect.Click
Try
connectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnDisconnect_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnDisconnect.Click
Try
disconnectSerialPort()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnSend_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnSend.Click
Try
connectedSerialPort.Write(txtSend.Text + vbCrLf)
txtSend.Text = ""
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_DataReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialDataReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.DataReceived
Try
' Received data from the serial port, send it for processing.
processIncomingData(connectedSerialPort.ReadExisting())
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub connectedSerialPort_ErrorReceived(sender As Object, e As SerialErrorReceivedEventArgs) Handles connectedSerialPort.ErrorReceived
Try
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnRefreshPorts_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnRefreshPorts.Click
Try
refreshPortsList()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
Private Sub btnClear_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles btnClear.Click
Try
txtReceive.Text = ""
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Returns if the serial port is currently connected.
''' </summary>
''' <value></value>
''' <returns></returns>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private ReadOnly Property isSerialPortConnected
Get
Return connectedSerialPort.IsOpen()
End Get
End Property
''' <summary>
''' Update whether or not each UI control should be enabled based on
''' the connection state.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub updateConnectedEnableFields()
Try
Dim isConnected As Boolean = isSerialPortConnected
btnConnect.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnDisconnect.Enabled = isConnected
ddlCOMPort.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnRefreshPorts.Enabled = Not isConnected
btnSend.Enabled = isConnected
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Connect to the selected serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub connectSerialPort()
Try
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex >= 0 Then
connectedSerialPort.PortName = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
connectedSerialPort.BaudRate = 9600
connectedSerialPort.WriteTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadTimeout = -1
connectedSerialPort.ReadBufferSize = 4096
connectedSerialPort.WriteBufferSize = 2048
connectedSerialPort.Parity = IO.Ports.Parity.None
connectedSerialPort.StopBits = IO.Ports.StopBits.One
connectedSerialPort.DataBits = 8
connectedSerialPort.Open()
End If
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Disconnect the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub disconnectSerialPort()
Try
connectedSerialPort.Close()
updateConnectedEnableFields()
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Detect available serial ports and update the COM port list.
''' </summary>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub refreshPortsList()
Try
' Keep track of the selected port so we can reselect it after fresh.
Dim currentlySelectedPort As String = ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem
' Get the available ports and update the dropdown list.
Dim availablePorts As Array = IO.Ports.SerialPort.GetPortNames()
ddlCOMPort.Items.Clear()
ddlCOMPort.Items.AddRange(availablePorts)
' Reselect the previously selected port as a default.
If currentlySelectedPort IsNot Nothing Then
If ddlCOMPort.Items.Contains(currentlySelectedPort) Then
ddlCOMPort.SelectedItem = currentlySelectedPort
End If
End If
If ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = -1 AndAlso ddlCOMPort.Items.Count > 0 Then
' No port selected but one is available, default to it.
ddlCOMPort.SelectedIndex = 0
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' Function to process incoming data from the serial port.
''' </summary>
''' <param name="incomingBuffer"></param>
''' <remarks></remarks>
Private Sub processIncomingData(ByVal incomingBuffer As String)
Try
If txtReceive.InvokeRequired Then
' On background (serial port) thread. Invoke a delegate to call this
' function again on the foreground (UI) thread.
Dim incomingTextDelegate As New ProcessIncomingTextDelegate(AddressOf processIncomingData)
Me.Invoke(incomingTextDelegate, New Object() {incomingBuffer})
Else
' On foreground (UI) thread. Process the message.
txtReceive.Text += incomingBuffer
End If
Catch ex As Exception
End Try
End Sub
End Class
The code within this post is released into the public domain. You're free to use it however you wish, but it is provided "as-is" without warranty of any kind. In no event shall the author be liable for any claims or damages in connection with this software.
Saturday, August 8, 2015
Servo Controller: Servo Control via Serial Monitor
Ultimately I want a very efficient method for the computer to control the servos, but in the short term I just need a simple way to send servo commands from the computer. The quickest way to start is to use the Serial Monitor window in the Arduino IDE!
First I define a new global variable so I can keep track of which servo I'm controlling.
int32 debugServoNumber = 0;
Within the main program loop I continuously check if characters were received over the serial line. If an input was found (.available() > 0), then I call readSerialInput() to check for a command.
void loop()
{
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
readSerialInput();
}
}
The readSerialInput() function parses the string that was submitted over the serial line and controls the servos based on those commands.
void readSerialInput()
{
String serialInputString = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
// Echo back the command.
Serial.println(serialInputString);
if (serialInputString.startsWith("s=")) // Servo
{
String servoNumberString = serialInputString.substring(2);
debugServoNumber = servoNumberString.toInt();
Serial.print("Debug servo:");
Serial.println(debugServoNumber);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("p=")) // Percent Value
{
String valuePercentString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_percent(valuePercentString.toFloat());
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("v=")) // Pulse Value
{
String pulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_pulseLength(pulseValueString.toInt());
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("u=")) // Upper Pulse Value
{
String upperPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setUpperPulseLength(upperPulseValueString.toInt());
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMaximumValue();
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("l=")) // Lower Pulse Value
{
String lowerPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setLowerPulseLength(lowerPulseValueString.toInt());
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMinimumValue();
}
return;
}
This approach is very straightforward to use for a person entering commands on the fly. However, I'll more than likely send binary values when I create the full-fledged servo software. It will no longer be human readable, but it will be faster.
Copyright (c) 2015 Clinton Kam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
First I define a new global variable so I can keep track of which servo I'm controlling.
int32 debugServoNumber = 0;
Within the main program loop I continuously check if characters were received over the serial line. If an input was found (.available() > 0), then I call readSerialInput() to check for a command.
void loop()
{
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
readSerialInput();
}
}
The readSerialInput() function parses the string that was submitted over the serial line and controls the servos based on those commands.
void readSerialInput()
{
String serialInputString = Serial.readStringUntil('\n');
// Echo back the command.
Serial.println(serialInputString);
if (serialInputString.startsWith("s=")) // Servo
{
String servoNumberString = serialInputString.substring(2);
debugServoNumber = servoNumberString.toInt();
Serial.print("Debug servo:");
Serial.println(debugServoNumber);
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("p=")) // Percent Value
{
String valuePercentString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_percent(valuePercentString.toFloat());
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("v=")) // Pulse Value
{
String pulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setToValue_pulseLength(pulseValueString.toInt());
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("u=")) // Upper Pulse Value
{
String upperPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setUpperPulseLength(upperPulseValueString.toInt());
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMaximumValue();
}
else if (serialInputString.startsWith("l=")) // Lower Pulse Value
{
String lowerPulseValueString = serialInputString.substring(2);
servos[debugServoNumber].setLowerPulseLength(lowerPulseValueString.toInt());
servos[debugServoNumber].setToMinimumValue();
}
return;
}
How to Use
Using the Serial Monitor I can give commands to my microcontroller.
First I select which servo I want to control:
s=0
I can also redefine the lower limit:
l=200
Or upper limit:
At any time I can switch servos:
s=2
And send new instructions to it, such as a specific pulse (rather than a percentage):
v=200
This approach is very straightforward to use for a person entering commands on the fly. However, I'll more than likely send binary values when I create the full-fledged servo software. It will no longer be human readable, but it will be faster.
Copyright (c) 2015 Clinton Kam
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)